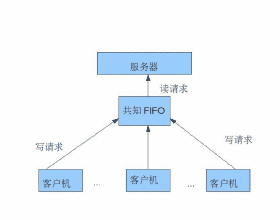
FIFO,又称作命名管道(named pipe),它是Linux系统中用于进程间通信的一种方法。
FIFO和pipe的区别在于:FIFO在文件系统中有对应的inode,可以通过ls命令查看。
sh-3.2# ls -lhF 。/fifo_file 100 prwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 1 1970 。/fifo_file| sh-3.2#
正因为它有一个名字,所以任何进程都可以访问它,所以FIFO可用于任意两个进程之间的通信。
pipe没有名字,在现有文件系统中无法查看到它的存在。
它只能用于父子进程、兄弟进程等具有血缘关系的进程间通信。
创建FIFO的方法如下:1. 调用umask系统调用来设定创建文件的权限,
#include 《sys/types.h》 #include 《sys/stat/h》 mode_t umask(mode_t mask);
2. 调用unlink系统调用先删除已经存在的fifo,
#include 《unistd.h》 int unlink(const char *pathname);
3. 调用mkfifo库函数去创建一个FIFO文件,
#include 《sys/types.h》 #include 《sys/stat.h》 int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
或者可以通过调用mknod系统调用并且指定参数mode为S_IFIFO也可以创建一个FIFO文件,
#include 《sys/types.h》 #include 《sys/stat.h》 #include 《fcntl.h》 #include 《unistd.h》 int mknod(const char *pathname, mode_t mode, dev_t dev);
1. 使用FIFO进行通信,每次传输的数据要限定在PIPE_BUF之内;
2. 对于FIFO的访问就像访问正规文件(regular file)一样,可以使用open/read/write/close等系统调用进行访问。
使用FIFO的应用有:1. 单纯的生产者/消费者问题,一个进程读数据,一个进程写数据;
2. 实现client/server架构的程序,客户端和服务器端通过FIFO进行通信。
上面就是Linux创建FIFO管道的方法介绍了,本文除了介绍了FIFO管道的创建外,还稍微介绍了下FIFO的使用及其注意事项,在使用的时候需特别注意。
以上就是在Linux下创建FIFO文件类型的详细内容,更多请关注CTO智库其它相关文章!
